Well exam was a pass 73%
The passing score changes during the year. So it was close.
In general if you can get your hands on a MAG it will be a lot easier.
Saar
Friday, February 8, 2013
Thursday, February 7, 2013
Learning Bytes
Learning Bytes
This is part of the Juniper partner portal.
These are small videos by the courseware people explaining items.
You can view them from
www.juniper.net/learningbytes
External port might be a public interface.
Ports are in NETWORK
Internal or External.
Their screen looks like this.
Enable ADMIN on external interface
/admin
In Source IP. You can enable the External Port.
You can also limit the access to to specific IPs like your home IP.
In - Maintenance >> Troubleshooting >> User Sessions >> Policy Tracing
Inside it you put the name
the realm
the source iP
and what you want to record.
Start Recording
Ok, let's say the user types in the wrong password.
On the - System >> Log/monitoring >> User Access logs
we can see there is a failure and it will say LDAP.
now if we go to ther
Policy TRACE
now if we click "view Log" we will see a LOT more detail like.
See for example.
username alex
bind failed to the user "wrong password"
sign in rejected.
e voila, you can tell the user he is a dummy and next time he should remember his password.
This is part of the Juniper partner portal.
These are small videos by the courseware people explaining items.
You can view them from
www.juniper.net/learningbytes
Using the External port for Admin Access Learning Byte
External port might be a public interface.
Ports are in NETWORK
Internal or External.
Their screen looks like this.
Enable ADMIN on external interface
/admin
In Source IP. You can enable the External Port.
You can also limit the access to to specific IPs like your home IP.
Policy Tracing Learning Byte
When to use the Policy tracing tool.
In - Maintenance >> Troubleshooting >> User Sessions >> Policy Tracing
Inside it you put the name
the realm
the source iP
and what you want to record.
Start Recording
Ok, let's say the user types in the wrong password.
On the - System >> Log/monitoring >> User Access logs
we can see there is a failure and it will say LDAP.
now if we go to ther
Policy TRACE
now if we click "view Log" we will see a LOT more detail like.
See for example.
username alex
bind failed to the user "wrong password"
sign in rejected.
e voila, you can tell the user he is a dummy and next time he should remember his password.
Random Questions
Question: 1
A customer wants to create a custom Junos Pulse configuration. Which two are required?
A. Connection set
B. Configuration set
C. Custom installer
D. Component set
Answer: A, D
Ok,
Junos Pulse is the software.
Remember it can do many things like acceleration and other things.
In this case we want to create a Custom configuration which will only have SOME of the items.
Instead of ALL of the items.
Lab3-3
- USERS > Junos Pulse > Connections > new Connection set
The connection determines the client settings.
Then in the next tab components
we select "new component set"
Then we select the "minimal components (only components needed to support the selected config are installed )
Answer C is a custom installer.
In OAC you can use a "preconfigured file" which does sound like a custom installer.
However the question was about Pulse.
Answer B
Configuration set. no such thing.
Question: 2
What type of firewall enforcers are supported by the Junos Pulse Access Control Service?
Answer SSG and SRX
The SRX was configured using the CLI
the SSG we did it using the Management GUI.
Question: 3
A customer is trying to decide which 802.1X inner protocol to use on their network. The customer
requires that no passwords be sent across the network in plain text, that the protocol be supported
by the Windows native supplicant, and that the protocol supports password changes at Layer 2.
Which protocol would meet the customer's needs?
A. EAP -TTLS
B. EAP -MD5
C. PAP
D. EAP -MSCHAPv2
Answer: D
This is more of an elimination challenge.
PAP is clear text so scratch it.
Windows is made by Microsoft , MS is short for Microsoft so MSchap would be supported by microsoft.
That is the answer.
Question: 4
You have a Junos Pulse Secure Access acting as an IF-MAP client, configured to federate all
user roles to a Junos Pulse Access Control Service acting as an IF -MAP Federation server.
A remote user using Junos Pulse logs in What happens next?
A. The Junos Pulse Secure Access Service redirects the user to the Junos Pulse Secure Access Service
for authentication
B. The Junos Pulse Access Control Service provisions enforcement points to enable resource access
for that user.
C. The Junos Pulse Secure Access Service publishes user session and role information to the IF-MAP
Federation server,
D. The Junos Pulse Secure Access Service provisions enforcement points to enable resource access
for that user.
Answer: C
The Answer is C easily simply because logically an IF-MAP client will update the IF-MAP server.
Question 5:
What is the first action you need to do after consoling in to the MAG appliance.
A. Set up a password
B. Set up an admin user
C. Import license
D. Select a personality.
The answer is D, you select either the SA or AC Access Control Service
What is the function of Host Enforcer?
A. To force clientless access to the network
B. To enforce restrictions on access to protected resources on the network
C. To scan an endpoints for compliance with security policies
D. To push a firewall policy to the endpoint's local firewall application
The answer is D. Host items run on the endpoint.
Host Checker will check the settings
Host Enforcer will configure the endpoint with your selection of rules.
Scott Newman, Courseware Developer
More questions from Juniper.
You are the administrator of a cluster.
You notice that the passive node takes a long time to respond and take over.
How do you improve the speed of change.
A. Change the inactivity timeout
B. Change the heartbeat
C. Change the Auth table timeout.
D. Change the number of ARP ping failures
Answer is D.
In the Cluster properties.
- System >> Clustering >> (click on the cluster) >> properties
there is a network healthcheck settings. In it you change the
"number of ARP ping failures before interface is disabled [3]
Auth table has nothing to do with this.
Heartbeat, the only heartbeat we have is from the AC to the AJAX Java agent and the
heartbeat of the Role Session parameters.
Inactivity timeout is from the Sessions
None of this is for Clustering Active/Passive except for D.
Question
Which of the two configuration settings will be the same on the two members of the Junos Pulse Access
Control Service Cluster.
A. Virtual Ports
B. User Roles
C. Authentication Server information
D. Routing tables.
Answer B and C
User Roles are synchronized.
Both devices must use the SAME authentication server.
So the settings will be identical.
Routing tables could be different depending on the location of the device.
Virtual Ports - there are no "virtual ports" on the MAG.
Question.
Where do you define the OAC configuration when creating a preconfigured install for the OAC.
OAC user interface
Odyssey settings
OAC administrator
OAC component set.
OK. Component set is from Junos.
The Odyssey settings are local to the endpoint
the OAC user interface is local to the endpoint.
So OAC administrator.
I quote "" to create an installer, you can use the OAC administrator to set the OAC configuration that you want, then export the settings into a zip file.
Options include hiding or disabling configuration icons, allowing users to modify adapter settings, or preventing them from disabling the OAC.
The installer also includes license keys.
So use the OAC administrator , create a customized OAC in a zip file.
Then use that as your preconfiguration file :
Question.
A user is running Linux which options can he use (two)
A. Java agent
B. Agentless
C. Odyssey access client
D. Junos Pulse.
Pulse - works for windows.
OAC - windows and MAC
Agentless - on everything.
Java agent - on anything that can run Java , since Linux can run Java.
The answers would be A and B.
Question.
You want to enable Guests some access. Which client would you offer them if you cannot install anything
on their laptops.
A. agentless
B. Host Checker
C. Anonymous
D. Junos Pulse.
Anonymous does jnot exist.
Host checker checks for compliance to the IMV only .
Pulse is a full client you must install
So Agentless A would be the correct choice.
Question.
You want to limit the number of features a ROLE will have in their Junos Pulse client.
What do you use to limit the number of features.
A. Junos Pulse connection type
B. Location awareness
C. Junos pulse client components.
D. Junos preconfiguration installer.
preconfigured or preconfiguration should ding OAC in your head.
connection type controls the connection
location aware will determine if the user is in the WAN , LAN or other.
Junos pulse has Client Components.
Role >> Junos pulse client components > New Component Set >>
junos pulse client components.
here you select the nice.
All components
No components
Minimal components which is just for the features you selected.
Question
Which three sign-in policy components are valid ?? Choose 3.
A. User Role Mapping
B. Host Enforcement
C. Authentication Protocol Set
D. Sign-in URL
E. Authentication Realm.
This is what a "NEW sign-in policy " window looks like.
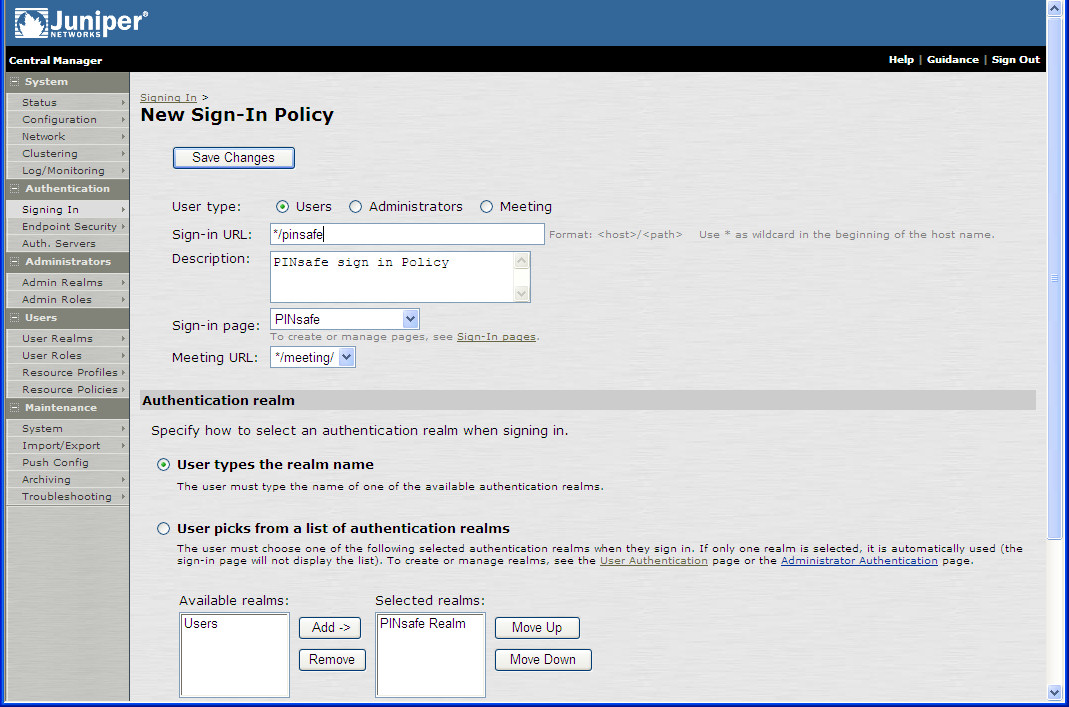
In it you create a SIGN-IN where users SIGN-IN.
So Sign-in URL should be easy to get.
Every sign-in page leads to some sort of Authentication Realm .(LDAP,Radius,none)
The last one is the Authentication Protocol Set.
(the top screenshot is for an SA and not an AC, sorry screenshots are scarce)
The Authentication protocol set is the option to add 802.1x to the sign-in
So all those 3 will give you the sign-in policy requirements.
Host Enforcement is on the
Host Checker Policy - which is under
>> Authentication >> Endpoint Security
User Role Mapping is done at the User Authentication Realms >>
Question.
OK, this one looks smart.
You administer the network , which has a NEW real using the Junos Pulse Access COntrol Service.
A User complains to you that they can access the network
but they cannot access the Accounting Server.
What are three explanations for this.
A. The user is being subjected to the Host Enforcer Policy
B. The User is subject to a role restriction.
C. The User is failing the host checker policy at the realm level.
D. The user is not mapped to the proper role.
E. The user is entering the incorrect authentication parameters.
So here you use the triage. The ITIL word for eliminating what cannot be possible.
E. The user is entering the incorrect password. - This cannot be because then he would not have ANY
access and we are told he can reach the rest of the network.
C. The user is failing the host checker policy at the REALM Level. - This cannot be because if he was
failing at the REALM level he would not be allowed in.
So the answers are the rest of the A,B,D
Questions
What are the Three Secure Access Control Service Enforcers.
A. Radius Enforcing Server
B. Host Enforcer
C. Infranet Enforcer
D. 802.1x Switch.
802.1X can enforce 802.1x authentication protocol Set.
Infranet Enforcer means the SSGor SRX Firewalls that can enforce IP source or IPSEC or other.
Host Enforcer can run on the client endpoint and enforce some rules of choice.
Radius is not an Enforcer it is an AUTHENTICATING SERVER
Question
You are creating ROLE mapping rules using your "local database" option.
Which two methods would you choose.
A. Group Membership
B. User Attributes
C. Certificates
D. Usernames
The catch here is the Local""
If it LDAP or remote then you would use Groups or Attributes.
HOwever since it is local.
Just use
USERNAME.
The CErtificates is a bit harder as I simply remembered there was an option for that in the lcoal database.
Yeah,
In the Local Database your choices when running the "role mapping rule"
are
Username.
Certificate
Custom Expressions.
Question
Which two parameters do you define for a user role.
A. Type of Agent Access methods
B. Custom user interface
C. Prohibited application.
D. Resource Policy.
So if you remember defining a user.
We selected what methods can he use like Pulse/ OAC/ Agentless
The last TAB was UI options where you can change the background and replace the Juniper image
with your company logo.
We don't have a "prohibited application" in the MAG.
Resource Policy is defined on the INFRANET ENFORCER
Comment
MAC Authentication Server.
MAC authentication Realm.
Both are unique to the MAC thing as you can tell by the big MAC in front.
The best EAP methods are.
EAP-TTLS
EAP-JUAC
EAP-MD5
EAP-GEneric Token Card.
So token card is with tokens
EAP-MD5 is very old from server 2000
Juac is the Juniper one and is the default.
TTLS is the best too.
Question.
On the MAG series device a Sensor event is configured with the action "replace user role" and make it permanent.
The MAG has quarantined a user based on a sensor event from an IDP.
In the MAG device GUI how do you release him from the Quarantine.
I'll save myself typing all the poisibilities.
It will NOT be in System>>Status >>Users simply because that would be the system users and not the
end users.
It will be in AUTHENTICATION > AUTH SERVERS >> srv >> tab users select the user
and click ENABLED to release the USER from Quarantine.
Question or reference to CAs

You might get some CA questions.
Remember.
o= organization.
In this example o=Verisign
C= country
ou= organizational unit. in LDAP this could be a group.
you should also look at Expiry times.
Expire on 01-07-2010 is no good.
FTP = SCP the only difference is the S for Secure Secure Copy Protocol.
There might be a few of these. MAG supports both.
Question
Set Security unified-access-control
Set access unified-access-control
Set services unified-access-control
set security UAC
Which is the correct one.
Very difficult to tell.
From the configs I remembered it was unified-access-control
Access I know is where you define access profiles for users and groups.
Security is where you define the zones and policies.
In the policy we had THEN permit application-services UAC-Policy
so I guess services.
EAP-TLS uses PKI
Wednesday, February 6, 2013
Chapter 12 -logging
Chapter 12 -logging
Tab called logs
Event Logs
system>>Logs/ monitoring
event logs system events
User Access log
Admin Access log is for admin items and changes
Sensor Log will be for events reported by the IDP.
Levels of logging.
Critical - is when the ADMIN cannot get in or most subsystems
Major - is when you lose some subsystems.
Minor - are individual request failures.
Info - when a user request is done or a modification to the device.
Each log has settings you can set as to what to log.
You can also set the size of the log.
In general you can also log externally.
syslog servers
You can set up filters and the format you want to use.
Standard
WELF
W2C
WELC-2.0 can add queries.
You can create custom log filters and apply them to the data being sent
A filter can set up the Query you want to run on the data.
In the log if you click an item it will filter it to a dynamic presentation.
You can also enable CLIENT logs
on the host checker
{}host checker.
System Status Dashboard
allows you to get a quick view.
Build
Config
logging disk
license and how many users are in.
memory and CPU.
SNMP tab.
You can download the MIB and install it.
You can set up traps.
You can enter the community.
The traps will be for what you select in the checkbox and you can specify to send major or critical events.
Statistics TAB
will show you a stat display by day/time.
Troubleshooting
Reachability (ping trace)
TCP dump
Event log - we talked about that.
Firewall Enforcer logs.
On the TOOLS you will have the reachability items.
ping
traceroute
nslookup fpr servers
ARP to find out MAC
RRTS round trip response times.
same place TP dump
will get all the TCP running on a port. - Basically sniffing.
You can output it to RAW or human readable which is more like WireShark.
On the Events >Log
we can see some tips on reasons.
To get Firewall Enforcer data we need to switch to the Firewall.
set services unified-access-control traceotions file ac1_trace.log
set services unified-access-control traceotions flag all
this will flag all events to the tracelog file which we can then open up and read.
Troubleshooting the USER interactions
You can turn on
{}Radius diagnostic logging.
and set up the size of it.
In maintenance > User Sessions > policy tracing
you can set up what events to log on for the MAG policy
you record it and then you view the LOG
To troubleshoot the IPSEC use
the logs on the Firewall enforcer
show log kmd
archiving Files
there is an option to archive your files.
You send them using SCP which is similar to ftp
You select what you want to archive and send it to an IP
either an archiving server or a local backup of the file.
This is all in Maintenance.
from the WEBui you can also export the configuration / users
You can also import.
You simply select the TARGET.
JTAC tools
TroubleShooting > System Snapshot
Remote Debugging allows the JTAC to access the system.
open a case from the support website.
View user Role assignment with the policy trace
See if you can reach items using the Troubleshooting >Tools
Exporting configuration files is in BINARY mode.
Tab called logs
Event Logs
system>>Logs/ monitoring
event logs system events
User Access log
Admin Access log is for admin items and changes
Sensor Log will be for events reported by the IDP.
Levels of logging.
Critical - is when the ADMIN cannot get in or most subsystems
Major - is when you lose some subsystems.
Minor - are individual request failures.
Info - when a user request is done or a modification to the device.
Each log has settings you can set as to what to log.
You can also set the size of the log.
In general you can also log externally.
syslog servers
You can set up filters and the format you want to use.
Standard
WELF
W2C
WELC-2.0 can add queries.
You can create custom log filters and apply them to the data being sent
A filter can set up the Query you want to run on the data.
In the log if you click an item it will filter it to a dynamic presentation.
You can also enable CLIENT logs
on the host checker
{}host checker.
System Status Dashboard
allows you to get a quick view.
Build
Config
logging disk
license and how many users are in.
memory and CPU.
SNMP tab.
You can download the MIB and install it.
You can set up traps.
You can enter the community.
The traps will be for what you select in the checkbox and you can specify to send major or critical events.
Statistics TAB
will show you a stat display by day/time.
Troubleshooting
Reachability (ping trace)
TCP dump
Event log - we talked about that.
Firewall Enforcer logs.
On the TOOLS you will have the reachability items.
ping
traceroute
nslookup fpr servers
ARP to find out MAC
RRTS round trip response times.
same place TP dump
will get all the TCP running on a port. - Basically sniffing.
You can output it to RAW or human readable which is more like WireShark.
On the Events >Log
we can see some tips on reasons.
To get Firewall Enforcer data we need to switch to the Firewall.
set services unified-access-control traceotions file ac1_trace.log
set services unified-access-control traceotions flag all
this will flag all events to the tracelog file which we can then open up and read.
Troubleshooting the USER interactions
You can turn on
{}Radius diagnostic logging.
and set up the size of it.
In maintenance > User Sessions > policy tracing
you can set up what events to log on for the MAG policy
you record it and then you view the LOG
To troubleshoot the IPSEC use
the logs on the Firewall enforcer
show log kmd
archiving Files
there is an option to archive your files.
You send them using SCP which is similar to ftp
You select what you want to archive and send it to an IP
either an archiving server or a local backup of the file.
This is all in Maintenance.
from the WEBui you can also export the configuration / users
You can also import.
You simply select the TARGET.
JTAC tools
TroubleShooting > System Snapshot
Remote Debugging allows the JTAC to access the system.
open a case from the support website.
View user Role assignment with the policy trace
See if you can reach items using the Troubleshooting >Tools
Exporting configuration files is in BINARY mode.
Tuesday, February 5, 2013
Junos Pulse access control administration guide
Junos Pulse access control administration guide
Great, another 800 pages on a PDF format.
Ain't being an IT person grand.
Overview.
The idea is you can leverage the MAG to control the clients that are allowed on the network.
The enforcement points that you can use are.
SRX/SSG firewalls
802.1x switches
802.1x Accesspoints
The End client itself can have a software called Host Enforcer.
IDP devices (optional)
You can also use the MAG to control devices that cannot authenticate using their MAC addresses.
The solutions is made from
IC device- in this case the MAG that pushes the policies to the enforcers.
UAC client- this client sits on the end device and works with the MAG
The types are.
Odysset client - this client is a software on the end device
Junos Pulse - this is the flagship software on the end device.
Java Agent - mainly for Linux support the Java will run the host checker
Agentless - it installs a temp agent that will run the host-checker.
Pulse itself also supports dynamic VPN and application acceleration.
Enforcers
ScreenOS can do layer 2 and 3
SRX layer 3
802.1x a wired network runs it.
802.1x a wireless network will associate you first and then run the 802.1x
IDP will review the traffic and can signal the MAG about bad traffic to close the session.
Ways of deploying the systems are.
the first one is Layer 2.
The device is in the LAN and will connect to the 802.1x authenticator which will use the MAG
as the Authenticating server.
The second is Layer 3.
The device is on the WAN and will connect using EAPover HTTP to the 802.1x authenticator.
Both of the above system will use the 802.x as the first item
then they will use the Firewall as the second enforcer.
The last way is without the firewall.
Just an 802.1x authentication.
How this is done.
You create policies.
The policies will control the access to the resources and the applications.
1. Succesful client check (host Checker)
2. Successful client authentication (RADIUS)
3. Successful client authorization (roles)
These are the requirements from the Manual.
Let's have a look and understand them.
install the IC series device. - This is pretty obvious. You will console into the device, you will set up an ip a subnet a gateway. The first step will be to select a personality either an AC or an SA.
basically enough connectivity to switch to the Web management.
Upgrade and license- upgrade is using your Jcare support you bought for the device (i Hope you did)
Lincesing is done using the hardware serial and your authorization code on their portal.
Install cetificates - the device, ssl, vpns in general most security and compliance requires the use of CA
certificates for the servers and clients to validate each other. So catch up on this theme.
Install the Enforcers. - Here you can choose. Firewall enforcer 802.1x or host enforcer.
Connect the MAG to the enforcer using the GUI
Configure an authentication server- obviously the list of users and passwords must come from somewhere.
local, radius, or LDAP using the RADIUS.
Set up resource policies for what will be protected.
Setup the IPSEC or IP enforcement this is for the Firewall enforcer.
configure the sign- in policies - like the host checker check
Configure the agents or OAC,Juniper JAVA
configure host checker
configure host enforcer optional this is the client that can protect the end client by controlling it.
pretty much those are the items.
Be sure to sync the clocks of all the devices so the authentication won't fail. (5 min)
Task guidance
on the right top corner you have the task guidance wizards to assist you on how to configure the devices.
IC series have administrator
read only administrator
users
those are pre-configured.
For each role you create you can specify which clients can use that role.
Then you can configure the settings for the agent or agentless for that role.
Pulse Component set.
All the components includes EES Enhanced Endpoint security + acceleration.
No components is for only updating Pulse.
Distribute to the users through a ROLE
Great, another 800 pages on a PDF format.
Ain't being an IT person grand.
Overview.
The idea is you can leverage the MAG to control the clients that are allowed on the network.
The enforcement points that you can use are.
SRX/SSG firewalls
802.1x switches
802.1x Accesspoints
The End client itself can have a software called Host Enforcer.
IDP devices (optional)
You can also use the MAG to control devices that cannot authenticate using their MAC addresses.
The solutions is made from
IC device- in this case the MAG that pushes the policies to the enforcers.
UAC client- this client sits on the end device and works with the MAG
The types are.
Odysset client - this client is a software on the end device
Junos Pulse - this is the flagship software on the end device.
Java Agent - mainly for Linux support the Java will run the host checker
Agentless - it installs a temp agent that will run the host-checker.
Pulse itself also supports dynamic VPN and application acceleration.
Enforcers
ScreenOS can do layer 2 and 3
SRX layer 3
802.1x a wired network runs it.
802.1x a wireless network will associate you first and then run the 802.1x
IDP will review the traffic and can signal the MAG about bad traffic to close the session.
Ways of deploying the systems are.
the first one is Layer 2.
The device is in the LAN and will connect to the 802.1x authenticator which will use the MAG
as the Authenticating server.
The second is Layer 3.
The device is on the WAN and will connect using EAPover HTTP to the 802.1x authenticator.
Both of the above system will use the 802.x as the first item
then they will use the Firewall as the second enforcer.
The last way is without the firewall.
Just an 802.1x authentication.
How this is done.
You create policies.
The policies will control the access to the resources and the applications.
1. Succesful client check (host Checker)
2. Successful client authentication (RADIUS)
3. Successful client authorization (roles)
These are the requirements from the Manual.
Let's have a look and understand them.
install the IC series device. - This is pretty obvious. You will console into the device, you will set up an ip a subnet a gateway. The first step will be to select a personality either an AC or an SA.
basically enough connectivity to switch to the Web management.
Upgrade and license- upgrade is using your Jcare support you bought for the device (i Hope you did)
Lincesing is done using the hardware serial and your authorization code on their portal.
Install cetificates - the device, ssl, vpns in general most security and compliance requires the use of CA
certificates for the servers and clients to validate each other. So catch up on this theme.
Install the Enforcers. - Here you can choose. Firewall enforcer 802.1x or host enforcer.
Connect the MAG to the enforcer using the GUI
Configure an authentication server- obviously the list of users and passwords must come from somewhere.
local, radius, or LDAP using the RADIUS.
Set up resource policies for what will be protected.
Setup the IPSEC or IP enforcement this is for the Firewall enforcer.
configure the sign- in policies - like the host checker check
Configure the agents or OAC,Juniper JAVA
configure host checker
configure host enforcer optional this is the client that can protect the end client by controlling it.
pretty much those are the items.
Be sure to sync the clocks of all the devices so the authentication won't fail. (5 min)
Task guidance
on the right top corner you have the task guidance wizards to assist you on how to configure the devices.
IC series have administrator
read only administrator
users
those are pre-configured.
For each role you create you can specify which clients can use that role.
Then you can configure the settings for the agent or agentless for that role.
Pulse Component set.
All the components includes EES Enhanced Endpoint security + acceleration.
No components is for only updating Pulse.
Distribute to the users through a ROLE
Chapter 9 - Configuring Layer 2 Enforcement
Chapter 9 - Configuring Layer 2 Enforcement
Requirements:
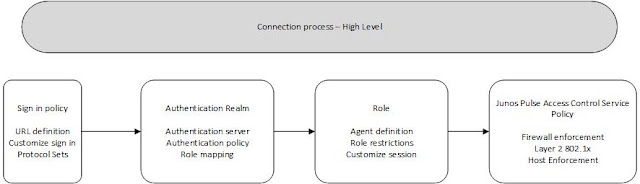

Requirements:
- Authenticator must support Dynamic configuration using the Radius attributes it will be getting back
- Authenticator must communicate with the Junos pulse Access control (Radius)
- 802.1x enabled on the device and the ports.
- Attributes like the VLAN must be configured on the device
- If assigning Vlans dynamically - a DHCP must be available for the VLANs
Example
Any employee goes on employee VLAN
contractor go on contractor VLAN
Failure or guest go on remediation VLAN.
Each device on route to the supplicant must be configured as an 802.1x layer 2 enforcer.
Adding the RADIUS server to the SRX.
system {
time-zone America/New_York;
}
radius-server {
172.16.0.101 {
secret "$9$zFusF9p0ORSlM1Rs4ZjPf1RhcyK"; ## SECRET-DATA
timeout 4;
retry 2;
source-address 1.1.1.12;
access {
profile AC1 {
authentication-order radius;
radius {
authentication-server 172.16.0.101;
OK. So the first one sets up the Radius server.
The second one creates an access profile. Sets up the order of authentication to use RADIUS
then adds the server to use. Which is the one we created first.
The second one creates an access profile. Sets up the order of authentication to use RADIUS
then adds the server to use. Which is the one we created first.
1.1.1.12 is the SRX
172.16.0.101 is the MAG Radius
On the 802.1X switch
protocols { # the stanza we will use
dot1x { # 802.1x
authenticator { # mark the switch as an authenticator
authentication-profile-name AC1; #profile access
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0 { # interface , usually you can mark all in the switch
supplicant single; #single supplicant can apply at a time.
guest-vlan REMEDIATIONVLAN; #guest vlan for non authenticated
server-reject-vlan REMEDIATION; # Vlan for rejected clients.
That way the REMEDIATION vlan can only have access to the Web
So they can correct their flaws like update the AV or the patches.
So they can correct their flaws like update the AV or the patches.
Configuring the 802.1x on the MAG
All of this will be applied on the initial connection as they connect.

The PROTOCOL Set is in the sign-in policy .
That is where we will configure it.
That is where we will configure it.
Steps.
Verify There is a Dictionary. - Remember the dictionary of attributes.
Each dictionary is a manufacturer one.
Each dictionary is a manufacturer one.
UAC > Network Access > Radius dictionary.
extreme.dct
juniper.dct
You can verify the RADIUS vendor list
This is only if you are not using the default list.
Add the Authentication Protocol Set
First select the Authentication Protocol , the order matters and it will try the EAP-TTLS first.
The specify the INNER authentication protocol to use.
In this case it will be under the TTLS block.
It will try EAP-JUAC the Juniper one first.
Then PAP
then CHAP
In this case it will be under the TTLS block.
It will try EAP-JUAC the Juniper one first.
Then PAP
then CHAP
Then it will try the EAP-PEAP here you specify the innter authentication too. It will show under the PEAP box.
In this case it is again EAP-JUAC.
In this case it is again EAP-JUAC.
the order matters.
Once you selected the Authentication protocol set
You will create or use the current Sign-in policy.
In the sign-in policy you will select the Authentication protocol you just created.
You select the Authentication protocol in the REALM. ---> Authentication protocol.
You will create or use the current Sign-in policy.
In the sign-in policy you will select the Authentication protocol you just created.
You select the Authentication protocol in the REALM. ---> Authentication protocol.
So I guess you apply it to the REALM.
Location Group
You can create a location group for people depending on where they sign in.
You can apply this sign-in policy to tha location group.
???
You need to configure EACH 802.1x authenticator as a RADIUS client.
uAC >> netowrk access > RADIUS client select the make and model and add a location group.
Next you can configure the RADIUS Attribute.
This is the ATTRIBUTE that will be sent from the RADIUS to the Authenticator once
you ahve made it.
This is the ATTRIBUTE that will be sent from the RADIUS to the Authenticator once
you ahve made it.
UAC >> Network ACcess > Radius Attributes
you create a policy and select the LOCATION group. Then you add the RADIUS attributes you want to add.
Then you can make it more granular by selecting which ROLES will this apply to.
Second Example.
You can add an attribute that the Device must be with so and so IP.
Pulse
Outer EAP-TTLS
inner EAP-JUAC
MAC authentication Server
authentication > AUTH server new MAC address authentication
add the MAC addresses.
add the MAC addresses.
or set up an LDAP server for the MAC addresses to be received from.
then
Create a new REALM
UAC > MAC address Realm. new
UAC > MAC address Realm. new
point to the MAC AUTH server you created.
then when the device comes in the user can select that realm
or you can apply that Realm to devices.
or you can apply that Realm to devices.
Location Group associates devices with a policy.
MAC Auth Server MAC auth Realm are only for MAC addresses.
Chapter 5 - user roles
User Roles.
We are looking at the ROLE part.
This is part of the Authorization. What is the role Authorized to...
A user role does not mean access to resources YET!!
You can create users manually in the Local Database of the MAG.

You can set a
start time
end time {these are for access times}
one time use {} the account will be disabled when he logs out.
enabled/disabled/quarantined {}
require user to change password {} must set up so users must change passwords
Creating ROLES
USERS>> user role >> new role.
If you leave the checkbox cleared it will take the default option.
{research this part}}
AGENT tab
In the agent tab you specify
In the AGENTLESS tab
You can enable the Agentless for this role
You can also disable the AJAx heartbeats.
In the GENERAL tab
You can set up
session options are for the session length + timeouts.
roaming session means they can change IP .
Persistent session adds a cookie to HD.
So when you close the explorer tab you can still reconnet.
Junos Pulse only disconnects when you log out.
{{All of the above says for example Employee role you can access only with OAC, depending
on what you chose}}
Customize UI.
You can change the Juniper LOGO to corporate logo background and add
session counter that says how much time you have left to the user in his pulse.
show notification message on the welcome page
show instructions for the users
Show copyright by juniper.
Role restriction
You can restrict the role to only IP network X.
You can restrict Browser type
You can restrict Certificate
You can restrict based on the result of the host checker.
Ok now you have role
The way of signing on.
The UI for hi
and restrictions of the role.
Verify the roles are set up in the User roles main window.
Role Mapping rules
Username - we did this above.
Group membership - ldap
Certificate attributes - expression
Custom Expressions- you can custom choose.
Role-mapping is in the Authentication Realm.
User realms >> users >> role mapping
You set up rules.
New Rule - When user meet these conditions assign these roles rulename stop
when username is ***** assign role contractor STOP will stop processing rules
or move to the next rule.
When you create the Role Mapping Rule. Your choices are based depending on the
servers that is the Authentication Realm.
For example for the local one - username, certificate and custom expressions are only available.
For example RULE = if username is ss*
then assign these roles
{available roles select}
{} stop
When you go back to the screen that shows all the rules you can select what happens
when more than one rule matches
Then
Users that do not meet any of the rules - will not be able to sign-in to the realm.
reorder rules using the up down arrows.
Sign In policy.
You can create a few policies
You can create different sign in pages with images,error messages, help files.
you can create a custom notification for each role
Creating the actual policy.
URL Sign-in page authentication Realms Enabled
*/admin/ Admin-page Admin Users V
*/ User-sign-in Users (802.1x) V
There is a NEW policy screen where the above will be selected from tabs.
specific rules come before rules
We are looking at the ROLE part.
This is part of the Authorization. What is the role Authorized to...
- Enable or disable the type of access you can have Pulse,OAC,clientless
- You can limit the type of access for the role.
For example if the role is accounting, then you must use Junos Pulse
and do not get that role if you are agentless. - Personalize your User Interface
- Set up user session parameters for the role.
A user role does not mean access to resources YET!!
You can create users manually in the Local Database of the MAG.
You can set a
start time
end time {these are for access times}
one time use {} the account will be disabled when he logs out.
enabled/disabled/quarantined {}
require user to change password {} must set up so users must change passwords
Creating ROLES
USERS>> user role >> new role.
If you leave the checkbox cleared it will take the default option.
{research this part}}
AGENT tab
In the agent tab you specify
- Should the MAG install an agent
- Junos
- odyssey
- Should you install java
- Should you enable the host enforcer
In the AGENTLESS tab
You can enable the Agentless for this role
You can also disable the AJAx heartbeats.
In the GENERAL tab
You can set up
session options are for the session length + timeouts.
roaming session means they can change IP .
- enable
- disable
- Limit to subnet This is ok for the LAN only
Persistent session adds a cookie to HD.
So when you close the explorer tab you can still reconnet.
Junos Pulse only disconnects when you log out.
{{All of the above says for example Employee role you can access only with OAC, depending
on what you chose}}
Customize UI.
You can change the Juniper LOGO to corporate logo background and add
session counter that says how much time you have left to the user in his pulse.
show notification message on the welcome page
show instructions for the users
Show copyright by juniper.
Role restriction
You can restrict the role to only IP network X.
You can restrict Browser type
You can restrict Certificate
You can restrict based on the result of the host checker.
Ok now you have role
The way of signing on.
The UI for hi
and restrictions of the role.
Verify the roles are set up in the User roles main window.
Role Mapping rules
Username - we did this above.
Group membership - ldap
Certificate attributes - expression
Custom Expressions- you can custom choose.
Role-mapping is in the Authentication Realm.
User realms >> users >> role mapping
You set up rules.
New Rule - When user meet these conditions assign these roles rulename stop
when username is ***** assign role contractor STOP will stop processing rules
or move to the next rule.
When you create the Role Mapping Rule. Your choices are based depending on the
servers that is the Authentication Realm.
For example for the local one - username, certificate and custom expressions are only available.
For example RULE = if username is ss*
then assign these roles
{available roles select}
{} stop
When you go back to the screen that shows all the rules you can select what happens
when more than one rule matches
Then
- Merge the settings
- User must select from among the assigned roles
Users that do not meet any of the rules - will not be able to sign-in to the realm.
reorder rules using the up down arrows.
Sign In policy.
You can create a few policies
You can create different sign in pages with images,error messages, help files.
you can create a custom notification for each role
Creating the actual policy.
URL Sign-in page authentication Realms Enabled
*/admin/ Admin-page Admin Users V
*/ User-sign-in Users (802.1x) V
There is a NEW policy screen where the above will be selected from tabs.
specific rules come before rules
Friday, February 1, 2013
JNCIS-AC labs
JNCIS-AC labs
Ok, labs with a notepad.
Sorry, that is life.
NSM express will run you around 3K used.
SRX 210 around $500
ssg 20 $200
Terminal server $500
MAG $5000
MAG CMC $5000
MAG 6611 Chassis $3000
You'll need the licenses etc.
and you can't find the stuff used.
You'll probably need the Jcare to update them.
Partners get a discount but to be honest your manager will probably collapse with a coronary
if you present him with the bill.
There is no virtual lab either.
You can try Ingram Micro or beg Juniper for some access.
The course lab is simple.
So the PC will have
Pulse
OAC
JAVA
Agentless
The Server will have the resources you want.
The firewall will handle the IPSEC and Enforcement point.
The AC will have the AC stuff.
First lab is to configure the MAG.
Connect the Console to the MAG.
The installation is
9600
no flow
The text will ask to proceed Y
Agree to the license Y
IP
Subnet
Gateway
DNS
DNS domain
WINS
is all of this correct Y.
So far easy.
Create a user ADMIN
password
Create a self certificate using
common name is server.domain.com
orgazniation name domain.com
random text and it will generate the certificate.
https://IP-ADDRESS/admin
Now if you still want to see the CLI
You get the options you can choose from using a number.
1. Network Tools like ping arp
2. Create Admin username password
3. Display log
4. System options.
5. Toggle password protection for the console
6. Create a super user that dumps the others and lets you in.
7. System snapshot for backup.
8. Reset encryption to a lower 40 so you can export it.
select 1 and 5 and you can ping a gateway.
Upgrading the Software.
Go to Juniper website and download the latest version.
Sign in
https://ac1.pulse.local/admin admin is for administrators without it it is for users.
Ok, labs with a notepad.
Sorry, that is life.
NSM express will run you around 3K used.
SRX 210 around $500
ssg 20 $200
Terminal server $500
MAG $5000
MAG CMC $5000
MAG 6611 Chassis $3000
You'll need the licenses etc.
and you can't find the stuff used.
You'll probably need the Jcare to update them.
Partners get a discount but to be honest your manager will probably collapse with a coronary
if you present him with the bill.
There is no virtual lab either.
You can try Ingram Micro or beg Juniper for some access.
The course lab is simple.
So the PC will have
Pulse
OAC
JAVA
Agentless
The Server will have the resources you want.
The firewall will handle the IPSEC and Enforcement point.
The AC will have the AC stuff.
First lab is to configure the MAG.
Connect the Console to the MAG.
The installation is
9600
no flow
The text will ask to proceed Y
Agree to the license Y
IP
Subnet
Gateway
DNS
DNS domain
WINS
is all of this correct Y.
So far easy.
Create a user ADMIN
password
Create a self certificate using
common name is server.domain.com
orgazniation name domain.com
random text and it will generate the certificate.
https://IP-ADDRESS/admin
Now if you still want to see the CLI
You get the options you can choose from using a number.
1. Network Tools like ping arp
2. Create Admin username password
3. Display log
4. System options.
5. Toggle password protection for the console
6. Create a super user that dumps the others and lets you in.
7. System snapshot for backup.
8. Reset encryption to a lower 40 so you can export it.
select 1 and 5 and you can ping a gateway.
Upgrading the Software.
Go to Juniper website and download the latest version.
Sign in
https://ac1.pulse.local/admin admin is for administrators without it it is for users.
Chapter 16 - Netscreen as enforcement firewalls
Chapter 16 - Netscreen as enforcement firewalls
In NetScreen OS you will see a Shield on the Policy that will indicate a infranet-auth policy invocation.
Source IP will match
Then permit will point to the INFRANET
the INFRANET will check if the traffic is allowed.
You can add VPN they recommend you configure it from the MAG.
Policies
Resource
IPSEC VPN
Source Interface
AUTH table mapping
IP address pool for the NAT.
Resource Policy defines which users can allow or deny to resource
AUTH table match the user request with the resource policies
Generic source policy on the enforcer
MAG pushes the resource policy to the nforcer
End user auth to the MAG
maps the roles
Same thing- the Enforcer does not know if you are allowed only that you need to check for permission.
The dropping and then querying is called
Dyanmic auth table allocation.
source IP policy : permit any any any infranet-auth
it is basically a placeholder that will call the MAG to provide the details of the access.
release 6.1 or later allows you to specify an IPSEC policy to a zone
less than that you need to each resource.
you need resource access policy
and VPN setup policy for it to work
You can map specific roles to low end devices so their Auth table does not overflow.
6.1 and above uses dynamic Auth table.
Source INTERFACE policy
is useful when the device is in transparent mode.
You can set up NAT with IP address pools.
If the device connecting is behind a NAT the MAG can give it a VIP address
to use for the IPSEC ???
On the UAC > Infranet enforcer you set up a IPSEC tunnel.
Then you set up a resource policy to the reousrce (ip)
apply it to your chosen roles.
then you can add additional AntiSpam-IDP-Antivurs from the firewall.
In the IPSEC policy you set up the virtual adapater if you want.
then apply it to the roles.
on the AUTh table Mpaping you can delete the default policy and limit it to specific roles.
on the IP address pools you set up the IP address pools for the VIP addresses that will be given to the VPN
Verify
>get policy id 1it will say permit-infranet-auth
> get auth table to see if there are any users
You need a IPSEC policy for each interface that can be receiving the traffic.
>get policy id 3
tunnel-infranet-auth status enabled.
In NetScreen OS you will see a Shield on the Policy that will indicate a infranet-auth policy invocation.
Source IP will match
Then permit will point to the INFRANET
the INFRANET will check if the traffic is allowed.
You can add VPN they recommend you configure it from the MAG.
Policies
Resource
IPSEC VPN
Source Interface
AUTH table mapping
IP address pool for the NAT.
Resource Policy defines which users can allow or deny to resource
AUTH table match the user request with the resource policies
Generic source policy on the enforcer
MAG pushes the resource policy to the nforcer
End user auth to the MAG
maps the roles
Same thing- the Enforcer does not know if you are allowed only that you need to check for permission.
The dropping and then querying is called
Dyanmic auth table allocation.
source IP policy : permit any any any infranet-auth
it is basically a placeholder that will call the MAG to provide the details of the access.
release 6.1 or later allows you to specify an IPSEC policy to a zone
less than that you need to each resource.
you need resource access policy
and VPN setup policy for it to work
You can map specific roles to low end devices so their Auth table does not overflow.
6.1 and above uses dynamic Auth table.
Source INTERFACE policy
is useful when the device is in transparent mode.
You can set up NAT with IP address pools.
If the device connecting is behind a NAT the MAG can give it a VIP address
to use for the IPSEC ???
On the UAC > Infranet enforcer you set up a IPSEC tunnel.
Then you set up a resource policy to the reousrce (ip)
apply it to your chosen roles.
then you can add additional AntiSpam-IDP-Antivurs from the firewall.
In the IPSEC policy you set up the virtual adapater if you want.
then apply it to the roles.
on the AUTh table Mpaping you can delete the default policy and limit it to specific roles.
on the IP address pools you set up the IP address pools for the VIP addresses that will be given to the VPN
Verify
>get policy id 1it will say permit-infranet-auth
> get auth table to see if there are any users
You need a IPSEC policy for each interface that can be receiving the traffic.
>get policy id 3
tunnel-infranet-auth status enabled.
Chapter 15 - Junos Pulse Chassis Management
Junos Pulse Chassis Management
So

The CMC Chassis Management is the top left corner.
It allows you to manage the Chassis itself.
This is available on the 6610 and 6611
Runs Junos OS.
Gives you a Visual representation of the Chassis.

Nice,
It says SA for Secure Access
and IC for UAC
SSO for all the modules.
Configuration
You need to console in
Run the EZsetup wizard
System Hostname CM2
Root password
Enable Telnet
Enable SSH [yes]
configure management EM0.0
IP
Subnet
Gateway
Configure SNMP [yes]
Contact information for the administrator
community name for the SNMP
Physical location optional
System time and date
Time zone [yes] you will select it from the list.
YES will configure the settings you have done.
OK from the device
root@CM2 > request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id local_cert
root@CM2 > request security pki generate-certificate-request certificate-id local_cert1 domain-name cm2.pulse.local subject
this will generate the certificate request which you can submit to the CA.
When you are done you can load the certificate to the CM-060 using FTP or SCP
load it to local storage
request security pki loacl-certificate load filename /var/tmp/cm.2.cer certificate-id local_cert1
edit goes into configure mode
#set system services web-managemenet https port 443 interface em0.0 pki-local-certificate LOCAL_CERT1
So we generated a key-pair
generated a certificate request based on the pair.
Sent this to a server and got back a file answer.
Uploaded this file to the CMC using FTP SCP
Then we loaded it up to device from a our upload location
Then associated it with HTTPS so this will enable https with the certificate on the interface.
Only the management port supports SSO
Clocks must be synchronized to 5minutes or less.
Add the certiifcate to the Auth Servers on the Service modules.
To configure SSO You need to configure the address.
Configure > System proerties > Blade Single Sign On
then change the FPC for each blade.
On each SM you need to import the same certificate you got on the CMC.
- System > Auth Servers Chassis Auth Server
upload certificate
Click to launch SSO and you will be in the device of your choice.
So
The CMC Chassis Management is the top left corner.
It allows you to manage the Chassis itself.
This is available on the 6610 and 6611
Runs Junos OS.
Gives you a Visual representation of the Chassis.
Nice,
It says SA for Secure Access
and IC for UAC
SSO for all the modules.
Configuration
You need to console in
Run the EZsetup wizard
System Hostname CM2
Root password
Enable Telnet
Enable SSH [yes]
configure management EM0.0
IP
Subnet
Gateway
Configure SNMP [yes]
Contact information for the administrator
community name for the SNMP
Physical location optional
System time and date
Time zone [yes] you will select it from the list.
YES will configure the settings you have done.
OK from the device
root@CM2 > request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id local_cert
root@CM2 > request security pki generate-certificate-request certificate-id local_cert1 domain-name cm2.pulse.local subject
this will generate the certificate request which you can submit to the CA.
When you are done you can load the certificate to the CM-060 using FTP or SCP
load it to local storage
request security pki loacl-certificate load filename /var/tmp/cm.2.cer certificate-id local_cert1
edit goes into configure mode
#set system services web-managemenet https port 443 interface em0.0 pki-local-certificate LOCAL_CERT1
So we generated a key-pair
generated a certificate request based on the pair.
Sent this to a server and got back a file answer.
Uploaded this file to the CMC using FTP SCP
Then we loaded it up to device from a our upload location
Then associated it with HTTPS so this will enable https with the certificate on the interface.
Only the management port supports SSO
Clocks must be synchronized to 5minutes or less.
Add the certiifcate to the Auth Servers on the Service modules.
To configure SSO You need to configure the address.
Configure > System proerties > Blade Single Sign On
then change the FPC for each blade.
On each SM you need to import the same certificate you got on the CMC.
- System > Auth Servers Chassis Auth Server
upload certificate
Click to launch SSO and you will be in the device of your choice.
Chapter 14 - Junos Pulse Access Control integration
IF-MAP transfers the session from the Secure Access
to the Access Control seamlessly.
The same thing happens when you access items protected by another Access Control Device.
This is done with a single Login.
IF-MAP is part of the TNC. Trusted Network Connect.
Only the Junos Access Control Service can server as an IF-MAP server.
For that you would need a license.
IF-MAP is a repository of information about the sessions, roles etc.
Each device can connect to the server and get a subset of choice of the data and also update
the server. So the Secure Access can put some data in and then the Access control can connect
use that data and apply it to its session.
Server IF-MAP license MAGX600-iFMAP you need to buy the license for this.
Okay in system IF-MAP overview
Select the - system > IF-MAP federation
Select the server from the choices
Then add clients that will communicate with this server. They need a password or certificate.
(IF-MAP clients do not need a license)
On a client.
Select IF-MAP client
Then add a server URL httsp://ac1.pulse.local/dana-ws/soap/dsifmap
Then add the user and password.
On the clients you set up an Export-Policy.
They will export it to IF-MAP data to the Server
On the clients you set up an Import-policy.
This will interpret the IF-MAP data from the server into roles.
On the IF-MAP client you can see the Active Users TAB
This will give you the data that is being IF-MAPed
On the IF-MAP server you can see the sessions that have been exported/published to it.
Same here.
NSM
Network Security Management.
This is basically an appliance currently that allows you to manage SRX and NetScreen.
You can buy it currently however they are phasing it out for the Junos SPACE
The Firewall has three ways of getting configuration data.
- This is the CLI or webmanagement of the device itself (obvious)
- Junos Pulse Access Control service - because we linked them.
- NSM - NSM centrally manages the firewalls.
It is best practice to make the NSM the authorative one.
Update the Pulse - you can click refresh policies
Avoid CLI changes to the devices that are under the NSM.
Avoid CLI changes to the devices that are under the NSM.
Now, we can add the Pulse to the NSM to make life easier.
Procedure is.
- Install the Junos Pulse Access Control device (MAG)
- As Junos Pulse Access Control Service on the NSM
- Configure and Activate the DMI agent on the Pulse Access Control
- Confirm connectivity and import the configuration into the NSM.
Let's see how its done.
DMI is a set of protocols that run on TCP.
Netconf , XML alarms and structured syslog.
One DMI agent is per device.
Netconf , XML alarms and structured syslog.
One DMI agent is per device.
Under the TAB DMI Agent.
{} Inbound if you are using SSH to manage the device.
{} outbound enabled if you are talking to the NSM
Set up the port to accept on which is 22 ssh
Set up the "outbound connections" primary, backup ports , device and HMAC key 7804
Admin Realm
{} DMI logging
{} DMI logging
STRM
STRM Security Threat response Manager
is basically an event collection and correlation point for collecting all the logs from the security
devices, this way you can view them centrally.
devices, this way you can view them centrally.
This helps associate security breaches with a user and not only an IP.
This is what it looks like
It has hardDrives to store the data of the logging.
Let's configure it.
This is done under
System > log/monitoring you add syslog servers
you can also filter what to log.
you can also filter what to log.
IDP
Juniper has IDP sensors either as dedicated devices.
Juniper has IDP sensors either as dedicated devices.
or on the SRX family.
*If the IDP is a stand alone IDP like the ones above.
Then you need to manually configure the list of IPs for the device to monitor
*If the IDP is a module on the Enforcer (SRX/SSG) then the module
will get the IPs to monitor from the Dynamic Auth table.
The IDP detects malicious traffic.
It notifies the Junos Pulse Secure Access Control Service.
Then you need to manually configure the list of IPs for the device to monitor
*If the IDP is a module on the Enforcer (SRX/SSG) then the module
will get the IPs to monitor from the Dynamic Auth table.
The IDP detects malicious traffic.
It notifies the Junos Pulse Secure Access Control Service.
Which will take an action on the user session.
{They will send the IP ports the attack, time and the severity}
Actions - So the actions you can take can be Manual (by looking at the Active USers)
Automatic - Drop him, disable the user, remediate the user to another role.
The Junos Pulse will display an error message to the disabled user.
Configuration
Configuration
Adding a standalone IDP sensor:
-System > configuration > SensorsAdd the sensor - The port on which to listen
-System > configuration > SensorsAdd the sensor - The port on which to listen
the password
Manually enter the addresses to monitor and the severity that you want. 1 to 5 5 is critical.
Adding a Sensor on an Enforcer:
You can also configure a Sensor on the INFRANET ENFORCER (firewall) by
-UAC > Infranet Enforcer > connection > enforcer
{} USE IDP module as sensor.
-UAC > Infranet Enforcer > connection > enforcer
{} USE IDP module as sensor.
This will use the DYN auth table for the choice of IPs to monitor.
Both have Severity filters that determine what level is reported to the Secure Access.
1-5
Both have Severity filters that determine what level is reported to the Secure Access.
1-5
Policies will be in the Configuration > Sensors > Sensor event policies
You create a RULE based on the IDP signals that come in .
You create a RULE based on the IDP signals that come in .
So EVENT
then action ignore/terminate/disable user/replace his role
Then you select on which ROLES to apply this rule.
On System>> Status>> Active Users
you can see the users and run manual actions on them or reenable them if you want.
So IF-MAP Advantages are
single Sign on
You can get service from any AC in the federation
You can move the Session from the SSL to AC seamlessly .
You can get service from any AC in the federation
You can move the Session from the SSL to AC seamlessly .
Chapter 13 - High Availability
In Junos Pulse.
A cluster pair is two unit
A cluster multiunit is more than two which means 4.
Cluster can be an Active/Active or an Active/Passive.
Active Passive
Always uses VIP
they sync the state
The Active device sends ARP to the VIP.
When it fails the Passive device will send ARP to the VIP.
Active/Active
Can be done with a
1. Load Balancer
2. DNS round robin- the negative about this is that in case of failure you lose 50% of traffic.
This also gives you more throughput but the same licensing.
Must be the same LAN IP SUBNET in order for that to work.
State synchronization is done using the internal NIC
Must be the same hardware the same OS version
All of the resources must be accessible to all of the devices.
Alright.
When to use VIP Virtual IP.
If you have Pulse and Odyssey they download a list of cluster members and will switch to the next one.
Agentless must use the VIP.
This is another case of using VIP.
This time for the enforcer.
You can either use the VIP address for it.
Or create many instances of the MAG for it. Because they are all in sync it does not matter.
Synchronizing the information from device to device.
Information is synched using the internal interface.
There is a cluster password.
New member will send a message to the existing server asking for a synchronization.
After that you must reconfigure node-specific settings.
Transient information can be synched using.
Unicast, Brocadcast or Multicast
Session data and enforcer status
Nodes will have the service pack, so when you update one it will update the others.
Doing this
A cluster license is not required on the first node
Only on the nodes that join the cluster.
So
System > Clustering > Join Cluster then add a cluster name password and name of the member.
You can click PROPERTIES on the cluster and switch it from Active/Active to Active/Passive
You can also set up an EXTERNAL VIP and an INTERNAL VIP.
For ACTIVE/ACTIVE to have a VIP you must use a loadbalancer.
You can set up Synchronization.
{}Logs
{} user sessions
{} last time access time for the user sessions
You can change the number of ARP ping failures before the interface is disabled from 3
{} disable the external interface when the internal one fails.
{} advanced settings will change the number of timeouts for the underlying cluster.
OK.
Adding cluster members and checking the status.
You can add a load balancer from the
system > Network > Load Balancer.
You can go to the next device
System>Clustering > Join Cluster
on the
system > Status
you can see a member status window
or you can go to the CLUSTER Tab to see their status.
Configuring the Cluster on the Firewalls.
For the Firewalls you can have Active/Active or Active/Passive
Active/Active does not support IPSEC
In the INfranet Enforcer
You can add two serial numbers to the Platform.
In the Firewall you simply replace the AC1 with the VIP address
or you create a number of infranet-controller
Ok.
So Active / Active does NOT need a VIP it will use the Load balancer
Active/passive if you have an internal IP use the internal VIP
If you have an external IP too then you need to create an External VIP too.
Synchronize the users is an options
So is the synchronize the log messages.
{}disable external when internal fails, this is for the active/passive.
Clustering STATUS
will show you who is set.
_system > clustering > load balancer
is where you define the load balancer and if it is between endpoints or the Enforcer.
A cluster pair is two unit
A cluster multiunit is more than two which means 4.
Cluster can be an Active/Active or an Active/Passive.
Active Passive
Always uses VIP
they sync the state
The Active device sends ARP to the VIP.
When it fails the Passive device will send ARP to the VIP.
Active/Active
Can be done with a
1. Load Balancer
2. DNS round robin- the negative about this is that in case of failure you lose 50% of traffic.
This also gives you more throughput but the same licensing.
Must be the same LAN IP SUBNET in order for that to work.
State synchronization is done using the internal NIC
Must be the same hardware the same OS version
All of the resources must be accessible to all of the devices.
Alright.
When to use VIP Virtual IP.
If you have Pulse and Odyssey they download a list of cluster members and will switch to the next one.
Agentless must use the VIP.
This is another case of using VIP.
This time for the enforcer.
You can either use the VIP address for it.
Or create many instances of the MAG for it. Because they are all in sync it does not matter.
Synchronizing the information from device to device.
Information is synched using the internal interface.
There is a cluster password.
New member will send a message to the existing server asking for a synchronization.
After that you must reconfigure node-specific settings.
Transient information can be synched using.
Unicast, Brocadcast or Multicast
Session data and enforcer status
Nodes will have the service pack, so when you update one it will update the others.
Doing this
A cluster license is not required on the first node
Only on the nodes that join the cluster.
So
System > Clustering > Join Cluster then add a cluster name password and name of the member.
You can click PROPERTIES on the cluster and switch it from Active/Active to Active/Passive
You can also set up an EXTERNAL VIP and an INTERNAL VIP.
For ACTIVE/ACTIVE to have a VIP you must use a loadbalancer.
You can set up Synchronization.
{}Logs
{} user sessions
{} last time access time for the user sessions
You can change the number of ARP ping failures before the interface is disabled from 3
{} disable the external interface when the internal one fails.
{} advanced settings will change the number of timeouts for the underlying cluster.
OK.
Adding cluster members and checking the status.
You can add a load balancer from the
system > Network > Load Balancer.
You can go to the next device
System>Clustering > Join Cluster
on the
system > Status
you can see a member status window
or you can go to the CLUSTER Tab to see their status.
Configuring the Cluster on the Firewalls.
For the Firewalls you can have Active/Active or Active/Passive
Active/Active does not support IPSEC
In the INfranet Enforcer
You can add two serial numbers to the Platform.
In the Firewall you simply replace the AC1 with the VIP address
or you create a number of infranet-controller
Ok.
So Active / Active does NOT need a VIP it will use the Load balancer
Active/passive if you have an internal IP use the internal VIP
If you have an external IP too then you need to create an External VIP too.
Synchronize the users is an options
So is the synchronize the log messages.
{}disable external when internal fails, this is for the active/passive.
Clustering STATUS
will show you who is set.
_system > clustering > load balancer
is where you define the load balancer and if it is between endpoints or the Enforcer.
Chapter 11 authentication
authentication >> auth servers
select the type
local - we used this
ldap -
NIS
ACE
RADIUS
AD - windows LDAP
anonymous Server
SiteMinder
Certificate
MAC address authentication which we used before.
So when the user SIGNS in he will specify which REALM to use
a REALM is associated with an Authentication Server
The Authentication server will very the user exists and give approval
The Authentication server will also send group attributes.
The Junos Pulse Access Control will evaluate role-mapping rules to see what role to apply to the group.
LDAP
NAME : # Give this server a name
LDAP server # give it an IP
LDAP port #give it a port 389 usually or 636 ssl
Backup Ldap1
Backup LDap2 #backup servers
LDAP server type
connection of Unencrypted/ LDAPS / TLS
Connection timeout
Search timeout
Active Directory is annoying in that it requires a username with permissions to search the ActiveDirectory.
So for AD mark the check box for Authentication and provide a user and password.
If you want to allow users to change their LDAP/AD passwords from the MAG you must
provide an Administrator account in this too.
You will specify a Base DN to start from
dc=sales,dc=bobcat,dc=com
You will specify a Filter like cn-user
Strip domain from users so users can use bobcat/David format.
It will remove the Bobcat and use it as the Domain.
You can determine group membership by setting up the
BASE DN
Filter
member attribute
query and 2 nested levels is the best practice.
Static or Dynamic.
RADIUS 1812 183
In this scenario the MAG is a client of the BIG radius
Name
NAS_identifier - is the name that the MAG will use when courting the RADIUS
Server IP
Port 1812
backup server if you want.
Radius Accounting
RADIUS authntication can be enhanced by using RADIUS accounting.
This is when you tell the RADIUS the user just logged in
You do this by sending a Start message after success singing in
and a STOP message after logging out/denied/tiemout/admin intervention.
This is the template you send that data as
You set up a template for returning the data
<USER>(<REALM>)|<ROLE SEP=
so user domain then the roles separated by a comma.
Active Directoy and NY authentication
Name
Primary Active Directory
backup
Domain
administrator
password for administrator to the AD.
Authentication using
Kerberos NTLM v2 NTLMv1
only Active Groups.
anonymous authentication
This is for guests.
You use this to limit resources for them.
only define the NAME
users >> user realm > new user realm
assign a server to it.
You can have different ones for each item.
authentication let's say Radius
directory/attribute: let's say AD
accounting : let's say Radius.
refresh the roles if you want every 60 minutes to see if there was any change.
{}So refresh role will be for new sessions
{}refresh resource policies might kill current sessions.
Create a policy
ip limit
user realms> AD realm >> authentication policy >:>>SSO
single sign on a checkbox.
Stations must be members of the domain.
You sign in to the workstation and your credentials will be used for the Junos Pulse.
Creating Role-mapping RULES
First one is Username so you can manually map usernames to roles.
like fred, bob, muhammad role IT engineers.
User Attribute is from the LDAP or Radius - Click update to see the attributes you can select
Certificate - map them based on scertificate attributes.
Group Membership - this is only for LDAP or AD.
o= organization
cn=container
ou=organizational unit
Try remembering AD and LDAP from Microsoft.
also o can be used for organization
C for country
The Rules are. IF user has any of the following attribute values.
The value can be IS or ISNOT
THEN assign him the role.
(select a role)
Chapter 10 - Endpoint defense
Chapter 10 Endpoint defense.
Basically the Host Checker feature
Host Checker is a client side agent that performs checks by collecting IMC integrity measurements then sends thos measurements to the IMV which is teh MAG.
It can also check software,signatures, third party DLL certificates or similar.
It is compliant with the TNC trusted network connect.
This works in two ways.
If the device has Junos/OAC it has IMCs
If the device is java or agentless MAG will send him the IMCs.
The IMCs collect data and send it to the IMV (MAG)
There are two ways of using it.
One on the Authentication REALM as the device is entering the network.
The second is on the ROLE. so if it does not meet the IMV it will not be given the role.
Deny or Fix(remediation)
Steps.
Create the Host Checker policies.
Apply the policies to the REALM or the ROLE
specify user access to the hostchecker client
set up loggin.
- authentication >> endpoint security >> host checker
autoupgrade option
and the package to use.
First ivs VIRUS it can check for the signatures of AV software. list is XML
Second is patch , you can get a patchdata.dat
Third you can update the ESAP. Endpoint security assessment plug-in.
Create the POLICY. of what to check.
Yo uwill specify what happens on every operating system and what checks will be done on it.
The checks will change based on the operating system
They are rule checks for example. Require latest AV
You can also set up Remediation options if those items are NOT met.
Ports
Process
Files.
Registry keys
MAC
MAchine certificate must have a CN of your domain for example.
Patch Assesment.
You can require ALL of the rules
ANY of the rules
or create rule-set combos.
REMEDIATION
you can offer manual or system.
Manual are instructions
Automatic are killing processes deleting files.
you can also send the reasons to the user.
After the user fails he will be given two options.
Try again or enter without a certain role.
Message
Your connection has failed and the remediation page.
EES is an additional scanning license Enhanced Endpoint security.
It protects against MALWARE and AV.
Setting up the policy on the realm.
user >Authentication Realms > user_realm
First is source IP
Browse limit
Certificate limit
Pssword limit
host checker resutls
Last is you can apply restrictions based on the host check results
so if they did not pass they only get a limited ROLE>
Chapter 8 - 802.1x
802.1X Layer 2 {key is to remember this is Layer 2}
802.1x
This is an IEEE standard for layer 2 Access Control and Authentication.
Defines a method of associating users with rights using Filter or Vlan assignment
Time to memorize.
Memorize the Supplicant / Authenticator/ Authentication server. You can use that for CCDA, or CISSP.
802.1x is based on the EAP Extensible Authentication protocol. This is a framework.
EAP(method) is the actual authentication mechanism used.
The Supplicant
will have some software installed on it
802.1x Junos Pulse or OAC or third party.
It cannot send any layer 3 till the 802.1x authorization has been completed.
The negotiation of 802.1x is done using EAP messages.
The Authenticator.Blocks all traffic till he has finished negotiating their access.
The request he receives is an EAP over LAN.
It extracts the identity of the user and credentials and sends them to the RADIUS
or authenticating server using a standard format.
The Authenticating server Will evaluate the credentials and can also return additional information
Like which VLAN to put him on or other instructions.
What is EAP
It is an enhancement to PPP
In layman terms.
You arrive at the gate.
You say Hell (EAP Start)
The guard says show me ID (EAP request identity)
You give him ID (EAP response)
The guard calls Security Room and asks if he can come in. (Radius request)
The Security Room says to the guard ask him a challenge (Radius Access Challenge)
The Security guard relays that to you.
You respond
The guard relays your response to the Security Room.
They say, let him in and give him this ID (optional)
The guard says success and gives you an ID (vlan)
Supported EAP.
EAP- TTLS this stands for Tunneled Transport Layer Security.
This is the default for OAC.
It has two phases.
The first one is where the Authenticating server presents a certificate X509 to the supplicant.
This will create a Secure Tunnel.
The second is the supplicant can go back to presenting its credentials.
EAP-JUAC is Juniper
and allows the OAC software to take advantage of the full set of features like host enforcer.
EAP-JUAC is the default protocol for the INNER protocol.
Junos pulse can support using the NAP for the 802.1x
Third party
EAP-TLS enables non-juniper supplicants to authenticate using the PKI
EAP-SoH is a statement of health, this works with windows.
To use EAP-SOH you must use EAP-PEAP as the outer protocol OAC/Pulse.
EAP-GTC for tokens
PAP plaintext passwords.
CHap microsoft CHAP EAP-MD5 EaP-MS-CHAPv2
Ok, the above mentioned an Inner Join and an Outer Join.
Inner Authentication
Outer Authentication.
(I am thinking Access joins, sorry)
Example 1:
Assign the Users a VLAN based on their LDAP group membership.
The pulse will push the VLAN 20 to the switch (Authenticator) who will assign it to the client
Example 2:
When you daisy chain a PC to a Phone to a switch. Each item will need a different VLAN.
1. The switches must support the dual VLAN assignment this is usually done with CDP/LLDP
2. Either use the phones 802.1x
3. or you can use the phones MAC by using a MAC database as the authentication realm.
Radius elements in 802.1x
The Juniper Radius is based on their older product called "Steel Belted Radius"
It is a license you can put on the MAG to enable the Radius on it or you can use an external RADIUS
server.
The RADIUS will receive the EAP messages from the supplicants.
It will perform authentication.
It will send out additional attributes (like the VLAN, enforcer settings)
The Switch 802.1x or AP will apply those setting to the supplicant session.
RADIUS servers include
Clients - these are the Authenticators 802.1x who apply for supplicants.
Vendors - list of client manufacturers like 802.1x Juniper switches or Cisco802.1x.
Dictionary - This is the list of attributes that we talked about that are available.
{{VSA vendor specific attributes}}}
Users - List of usernames and passwords. They can also query an external server for those like AD/Ldap
Radius Proxy allows the MAG to use an external Authenticating Server (RADIUS)
The MAG will "proxy" the request to it and then update the Authenticator.
The Data from the MAG to the AAA in the "inner tunnel" is cleartext.
The Junos MAG will add the attributes based on the ROLE
MAC Authentication for client-less devices.
First problem with MAC authentication is user spoofing.
You can set up separate VLANs for the devices so they cannot cross into the corporate LAN.
You can also set up Packet Filters so they can only run specific protocols .
You must have a database with all the MACs required.
Great BAY BEacon Endpoint profiler - is a product that can analyze the endpoints
It identifies them and can tell if they can run the 802.1x or need MAC authentication.
It can mine data from those devices for the monitoring part.
It helps facilitate mobility of those devices.
Beacon can help with compliance in strict security settings.
set system radius-server x.x.x.x secret
set profile ac1
authentication-order radius
radius { authentication server x.x.x.x.}
the radius is the MAG.
On the switch
set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name AC1 interface ge-0/0/2
supplicant single
re-authentication 3600
guest-vlan remediation
server-reject-vlan remediation
guest is for unauthenticated
server reject is for failed authentication.
Radius-dictionary creates values that specific manufacturers can use.
802.1x TTLS PEAP for clients
802.1x MD5 TLS for phones.
Junos Pulse
Outer EAP-TTLS
inner EAP_juac
802.1x
This is an IEEE standard for layer 2 Access Control and Authentication.
Defines a method of associating users with rights using Filter or Vlan assignment
Memorize the Supplicant / Authenticator/ Authentication server. You can use that for CCDA, or CISSP.
802.1x is based on the EAP Extensible Authentication protocol. This is a framework.
EAP(method) is the actual authentication mechanism used.
The Supplicant
will have some software installed on it
802.1x Junos Pulse or OAC or third party.
It cannot send any layer 3 till the 802.1x authorization has been completed.
The negotiation of 802.1x is done using EAP messages.
The Authenticator.Blocks all traffic till he has finished negotiating their access.
The request he receives is an EAP over LAN.
It extracts the identity of the user and credentials and sends them to the RADIUS
or authenticating server using a standard format.
The Authenticating server Will evaluate the credentials and can also return additional information
Like which VLAN to put him on or other instructions.
What is EAP
It is an enhancement to PPP
In layman terms.
You arrive at the gate.
You say Hell (EAP Start)
The guard says show me ID (EAP request identity)
You give him ID (EAP response)
The guard calls Security Room and asks if he can come in. (Radius request)
The Security Room says to the guard ask him a challenge (Radius Access Challenge)
The Security guard relays that to you.
You respond
The guard relays your response to the Security Room.
They say, let him in and give him this ID (optional)
The guard says success and gives you an ID (vlan)
Supported EAP.
EAP- TTLS this stands for Tunneled Transport Layer Security.
This is the default for OAC.
It has two phases.
The first one is where the Authenticating server presents a certificate X509 to the supplicant.
This will create a Secure Tunnel.
The second is the supplicant can go back to presenting its credentials.
EAP-JUAC is Juniper
and allows the OAC software to take advantage of the full set of features like host enforcer.
EAP-JUAC is the default protocol for the INNER protocol.
Junos pulse can support using the NAP for the 802.1x
Third party
EAP-TLS enables non-juniper supplicants to authenticate using the PKI
EAP-SoH is a statement of health, this works with windows.
To use EAP-SOH you must use EAP-PEAP as the outer protocol OAC/Pulse.
EAP-GTC for tokens
PAP plaintext passwords.
CHap microsoft CHAP EAP-MD5 EaP-MS-CHAPv2
Ok, the above mentioned an Inner Join and an Outer Join.
Inner Authentication
Outer Authentication.
(I am thinking Access joins, sorry)
Example 1:
Assign the Users a VLAN based on their LDAP group membership.
The pulse will push the VLAN 20 to the switch (Authenticator) who will assign it to the client
Example 2:
When you daisy chain a PC to a Phone to a switch. Each item will need a different VLAN.
1. The switches must support the dual VLAN assignment this is usually done with CDP/LLDP
2. Either use the phones 802.1x
3. or you can use the phones MAC by using a MAC database as the authentication realm.
Radius elements in 802.1x
The Juniper Radius is based on their older product called "Steel Belted Radius"
It is a license you can put on the MAG to enable the Radius on it or you can use an external RADIUS
server.
The RADIUS will receive the EAP messages from the supplicants.
It will perform authentication.
It will send out additional attributes (like the VLAN, enforcer settings)
The Switch 802.1x or AP will apply those setting to the supplicant session.
RADIUS servers include
Clients - these are the Authenticators 802.1x who apply for supplicants.
Vendors - list of client manufacturers like 802.1x Juniper switches or Cisco802.1x.
Dictionary - This is the list of attributes that we talked about that are available.
{{VSA vendor specific attributes}}}
Users - List of usernames and passwords. They can also query an external server for those like AD/Ldap
Radius Proxy allows the MAG to use an external Authenticating Server (RADIUS)
The MAG will "proxy" the request to it and then update the Authenticator.
The Data from the MAG to the AAA in the "inner tunnel" is cleartext.
The Junos MAG will add the attributes based on the ROLE
MAC Authentication for client-less devices.
First problem with MAC authentication is user spoofing.
You can set up separate VLANs for the devices so they cannot cross into the corporate LAN.
You can also set up Packet Filters so they can only run specific protocols .
You must have a database with all the MACs required.
Great BAY BEacon Endpoint profiler - is a product that can analyze the endpoints
It identifies them and can tell if they can run the 802.1x or need MAC authentication.
It can mine data from those devices for the monitoring part.
It helps facilitate mobility of those devices.
Beacon can help with compliance in strict security settings.
set system radius-server x.x.x.x secret
set profile ac1
authentication-order radius
radius { authentication server x.x.x.x.}
the radius is the MAG.
On the switch
set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name AC1 interface ge-0/0/2
supplicant single
re-authentication 3600
guest-vlan remediation
server-reject-vlan remediation
guest is for unauthenticated
server reject is for failed authentication.
Radius-dictionary creates values that specific manufacturers can use.
802.1x TTLS PEAP for clients
802.1x MD5 TLS for phones.
Junos Pulse
Outer EAP-TTLS
inner EAP_juac
Chapter 7 - Firewall Enforcement
So on the last box.
Access Control Service Policy.
Firewall Enforcement
Host Enforcement.
802.1x (comes later on)
MAG Secure Acecss can send items to the
Firewall, like Set up the IPSEC VPN
Firewall, set up a resource access
Client, Host Enforcer - Set up a rule on the host. like block certain incoming TCP.
Enforcement
Source IP - Control Access based on source destination IP, protocol, ports
{no encryption}
Does not support third party ??
IPSEC
The Firewall uses IKE and can use the XAUTH to validate the user credentials. Pulse.
ESP or AH {AH does not do encryption}
So let's see a sample configuration on the SRX.
set security policy from-zone WAN to-zone LAN policy access_ac source any
set security policy from-zone WAN to-zone LAN policy access_ac destination ac1
then permit
set security policy from-zone WAN to-zone LAN policy any_resource source any
set security policy from-zone WAN to-zone LAN policy access_ac destination any
then permit application-services unified access control.
First rule, fine, get in, go to the ac1 and login.
Second rule. Nah, can't come in unless you went to the ac1
They recommend setting up
Junos Pulse AC service IPSEC first
General VPN second
Source IP third.
Associating a given user with a policy occurs during the role-mapping
Junos Pulse will build a table.
The table will match the user to the polcy rules.
It is merely creating the rules and not enforcing them.
It evaluates the policies only.
When the user types in the sign-in page.
After the user authentication.
When the user requests a resource enforcer will check
when the host checker changes.
So when you make any changes to the MAG unless any of the above happens the
users will still have the same access.
Pulse OAC
At the start enforcer does not know if you are allowed it only knows to consult the MAG appliance.
There is an AUTH table where the data is cached.
This is called Dynamic Authentication table allocation.
Resource Access
Auth tables on the Enforcers match the User role with the resource access required.
The policies are distributed by the MAG to the enforcers.
Endpoint tries, he is dropped, the SRX tells the MAG about this.
The MAG sends a policy to the Auth Table
next retry the endpoint is allowed in.
{{If the DNS is behind the enforcer it might create DNS timeout issues.}}
So basically the SRX is set up as normal.
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match source any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match destination any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match application any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource then permit
permit
{ application-services
uac-policy
}
So the uac-policy is the AUTH table.
It basically tells the traffic match to then match the AUTH table.
The AUTH table will have the permit to the resource and the user role allowed.
IPSEC to resource.
Must have both an IPSEC policy and the resource policy for it to work.
Host Enforcer is on the MAG
when you connect with the OAC it will push it to you.
Auth Policy
Either Dynamic which will be for all.
or you can set up the enforcer to support certain roles so you can limit the size.
If the Devices Enforcer and client are in between NAT you can use the NAT IP Address pools.
Firewall Enforcer Configuration
Basically the usual first part.
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match source any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match destination any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource match application any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy access_resource then permit
permit
{ application-services
uac-policy
Set up the MAG as the Radius Server
set access profile Employees authentication-order radius
set access profile Employees radius-server 172.16.15.1 secret password
set up the IKE phase 1 parameters
set security ike proposal Employee authentication-method pre-shared-keys
set security ike proposal Employee authentication-method pre-shared-keys
set security ike policy Employee mode aggressive
set security ike policy Employee pre-shared-key ascii-text passwordIPSEC
set security ike gateware Employee ike-policy Employee
set security ike gateware Employee ike-policy hostname endpoint.pulse.local
set security ike gateware Employee ike-policy xauth access-profile Employees
set security ipsec proposal Employee protocol esp
set security ipsec policy Employee proposals Employee
set security ipsec vpn pulse ike gateway Employee
set security ipsec vpn pulse ike ipsec-policy Employee
set security ipsec vpn pulse ike estblish-tunnels immediately
NOW
Basically the usual first part but this time it leads to the tunnel
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy TUNNEL match source any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy TUNNEL match destination any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy TUNNEL match application any
set security policies from zone wan to zone lan policy TUNNEL then permit
permit
{tunnel ipsec-vpn pulse}
{application-services
uac-policy}
the above was on the enforcer, pretty easy to tell today as it used JUNO.
Now on the MAG.
You need to configure this too.
You need to configure this too.
UAC --> Infranet Enforcer {This is where most of the SRX firewall items are} --> resource Access
resource --> new policy
name
description
resources
Infranet Enforcers -- map out which Infranet Enforcers will be enforcing this.
Which roles will have this policy applied to them.
Allow/Deny
You can add additional enforcer options {web/anti-spam/av/logging/idp}
Next tab is IPSEC
you can set up the IPSEC tunnel which will be created when you want to access that resource.
you can set up the IPSEC tunnel which will be created when you want to access that resource.
Specify the enforcer
Specify the roles this will apply to .
AUTH table mapping allows you to map
specific items to specific user roles this way you can keep the table nice and short.
specific items to specific user roles this way you can keep the table nice and short.
IP address pools.
For the above settings you can aslo force the enforcer to use an IP from the NAT pool.
Then again add that to the relevant enforcers
For the above settings you can aslo force the enforcer to use an IP from the NAT pool.
Then again add that to the relevant enforcers
then add it to the relevant roles.
host Enforcer.
UAC >> host enforcer
You set it up,
you select the resources
you select the resources
{{on this you set up the rules you want the enforcer to run.
<protocol>:<host>:<netmask:<destination ports>:<source ports>:
You apply it to the roles.
Verify
show services unified-access-control authentication-table
show security ipsec statistics
show security ike security-associations
User access logs
Pulse diagnostic viewer.
pdv.exe
from the OAC you can run diagnostics.
Captive portal is only for http
set services unified-access-control captive-portal guests
redirect-traffic-unauthenticated
redirect-rul httsp://x..xx.x./guest
set policty
then permit application-services uac-policy captive-portal guests
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





























